IoT and IIoT: Differences and Technologies Used
Internet of Things (IoT) and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are technologies that operate under the concept of the internet of things. Both enable devices to connect to the internet, but they have different application areas and technologies.
IoT (Internet of Things):
IoT is generally about connecting devices used in daily life to the internet. It can include a variety of devices, from home appliances to wearable technologies to smart city solutions. For example, devices such as home thermostats, security cameras, and lighting are typical examples of IoT. IoT is used for purposes such as making consumers' lives easier, increasing energy efficiency or increasing security.
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things):
IIoT refers to connecting devices used in industrial environments to the internet. It includes devices used in industrial environments, from factories to facilities to power generation facilities.
Devices such as industrial sensors, data collection devices, and manufacturing machines are examples of IIoT. IIoT is often used to increase productivity and profitability in industrial processes, such as improving production efficiency, improving maintenance processes, and optimizing production lines.
Technology Differences:
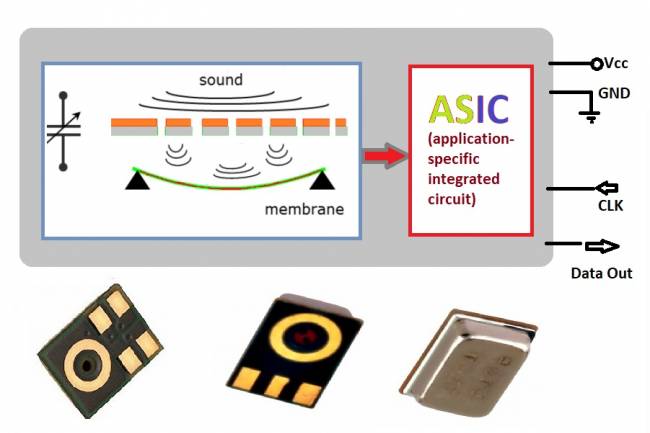
IoT devices are usually equipped with a microcontroller (MCU) or microprocessor. These are low-power devices typically used in homes or small-scale applications.
On the other hand, IIoT devices are designed to suit more complex industrial requirements. IIoT devices may have features such as more powerful processors, more memory, and more ports. They are also designed to support industrial protocols and may have more robust physical designs to meet industrial safety standards.
In conclusion, while IoT and IIoT are based on similar technologies, they differ in terms of application areas and technologies used. While IoT is generally consumer-oriented, IIoT is designed more for industrial and commercial uses. These differences are reflected in the design, functionality and usage areas of the devices.