What is a diode? What are its types and uses?
Diodes are the most basic circuit elements used in electronics. In the simplest terms; They are circuit elements that pass current in one direction and do not pass current in the opposite direction.
Diodes are responsible for performing different functions in different electronic systems due to their different properties.
Diodes are electronic components made of semiconductor materials. Generally, semiconductor materials such as silicon or germanium are used. These materials show different properties from metals and insulating materials in terms of electrical conductivity.
The basic structure of diodes consists of a combination of n-type and p-type semiconductor materials. This junction point is called the p-n junction and this is where the working principle of the diode lies.
In terms of their physical size and shape, diodes are produced in different standards:
Radial diodes: These cylindrical diodes have two wire legs and are connected to the circuit board by soldering.
SMD (Surface Mount Device) diodes: Surface mount diodes are smaller in size and are placed directly on the surfaces on the board. These diodes do not have legs, instead they have small soldering surfaces.
DO-35 diodes: They are generally used as signal diodes and have a cylindrical shape. They have two legs and are connected by soldering like radial diodes.
DO-41 diodes: These diodes, which are cylindrical in shape and similar in size to radial diodes, are especially used as power diodes.
TO-220 diodes: These diodes, which are frequently preferred in the use of transistors, are designed for high power applications. They have a 3-legged structure and are mounted by screwing to the cooler.
SOT-23 diodes: They are surface mount small size diodes and they are mainly used in mobile devices and other small devices.
Here are some types of diodes, the most common types:
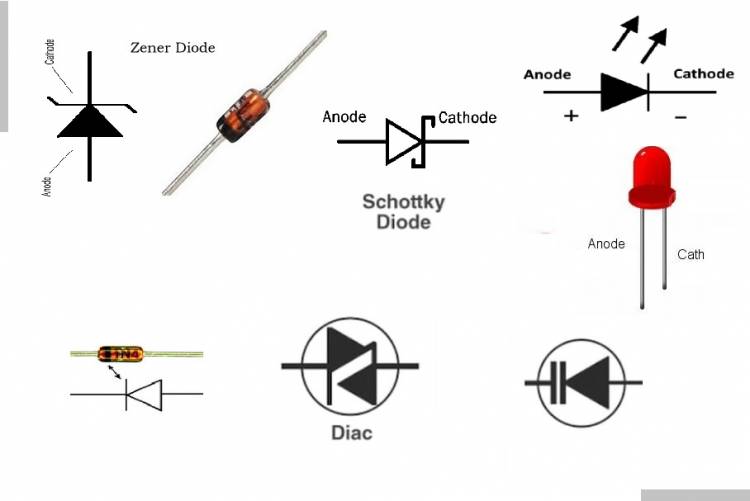
Zener diodes: It is a special diode that allows a sudden voltage drop in the reverse direction when it exceeds a certain voltage. They are used in voltage regulation and voltage stabilization circuits. For example, in a power supply circuit, the Zener diode is used to cut off the overvoltage when the voltage exceeds a certain value. We have published an application about Zener diode on our site: Related link: How to make a voltmeter?
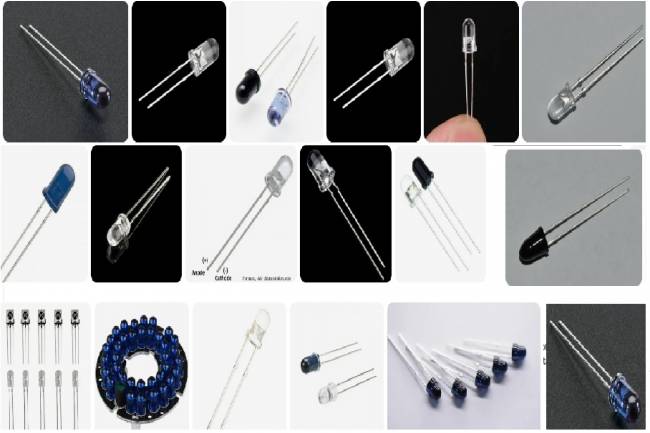
LED (Light Emitting Diode) diodes: They are diodes that convert electrical energy into light. They are widely used for lighting, instrument panels, displays and signaling purposes.
Silicon diodes: A standard diode and the most commonly used diode type. While they pass current in the direction of the voltage between their ends, they do not allow current to flow in the opposite direction.
Schottky diodes: Diodes made from a combination of metal and semiconductor materials. They are ideal for fast switching applications as they have a low voltage drop. For example, they are used in high-speed computer memories and power supplies.
Diac diodes: A special type of diode that allows current to flow in both directions. It is used in voltage control circuits.
Varicap diodes: It is the type of diode in which the capacitance values change depending on the applied voltage. They are used in applications such as signal frequency modulation (FM), television and radio broadcasting.
Here are some examples of diodes by special code names:
Zener diodes: 1N4728A, BZX55C9V1, 1N5339B
LED (Light Emitting Diode) diodes: 5mm blue LED, red light LED, green light LED
Silicon diodes: 1N4148, 1N4001, 1N5408
Schottky diodes: BAT54, 1N5711, SB5100
Diac diodes: DB3, BZY97C, 2N5060
Varicap diodes: BB112, BB209, BB329