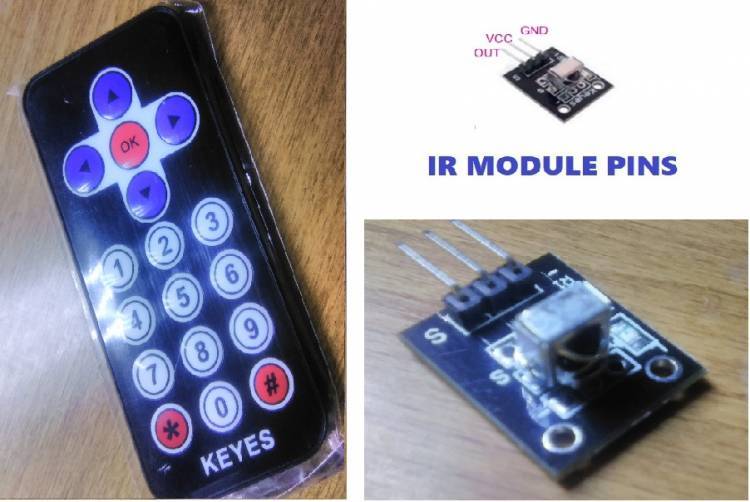
What is IR LED?
IR LED, infrared LED, is an electronic component that works by emitting infrared light. These LEDs produce light at wavelengths longer than the visible wavelength and are often used for remote controls, security systems, medical devices, industrial control systems, and other similar applications.
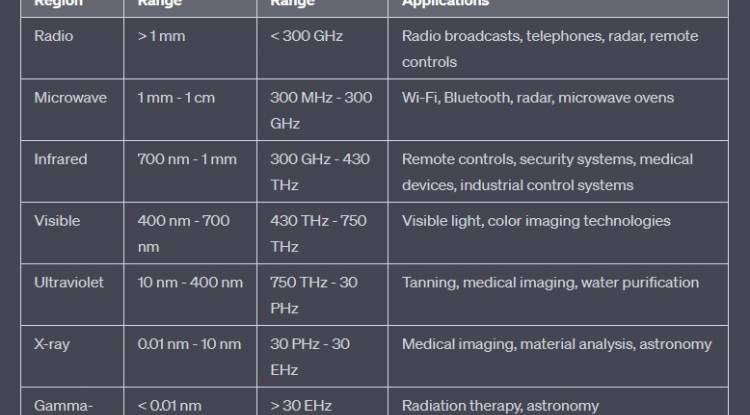
The infrared light emitted by IR LEDs cannot be perceived by the human eye. However, these rays can be received by some sensors and thus, remote controllable devices can be controlled. The wavelength of IR LEDs can vary depending on their intended use and typically ranges from 700 to 1000 nanometers.
Let's examine the electromagnetic spectrum table in the picture. Thus, we can understand the radiation in the wavelength emitted by IR LEDs:
What is the structure of IR leds?
IR LEDs are electroluminescent diodes mostly made using semiconductor materials such as aluminum, arsenic, and gallium. IR LEDs are manufactured by combining positive (P-type) and negative (N-type) semiconductor materials to form a PN junction.
N-type semiconductor material contains excess electrons while P-type semiconductor material contains excess holes. This PN junction causes electrons to move towards the P-type material and holes with holes move towards the N-type material. This movement causes electroluminescence, a phenomenon that produces infrared light.
IR LEDs are housed in a protective case and are often covered with glass or plastic lenses to increase light intensity.
What is electroluminescence?
Electroluminescence is the emission of light as a result of electrical excitation of a material. When a material recombines a high-energy electron with a charge hole, this reaction produces light by emitting a photon. This reaction occurs in semiconductor materials, as in IR LEDs.
The electroluminescence reaction of IR LEDs occurs by recombination of the separated charges in the PN junction. The holes in the P-type semiconductor material combine with the excess electrons in the N-type semiconductor material to collect in a PN junction. This aggregation results in electrons with excess energy recombining with holes, thereby emitting infrared light, called electroluminescence.
We have published an educational video about IR LEDs in the Electronic Laboratory category on our site. Comprehensive application of IR LEDs can be viewed from the link below: