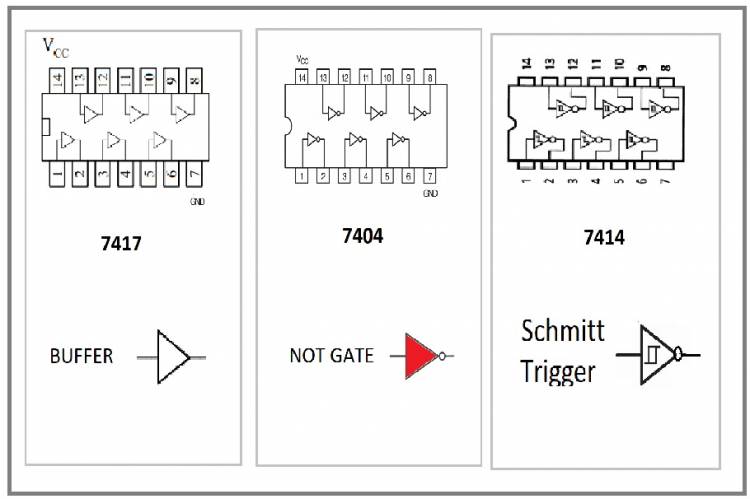
Logic Circuit Elements: Differences Between NOT, Buffer and Schmitt Trigger
NOT, Buffer and Schmitt trigger are basic logic elements used in digital circuits. Each performs a specific function, but they have different properties.
1. NOT (Inverter):
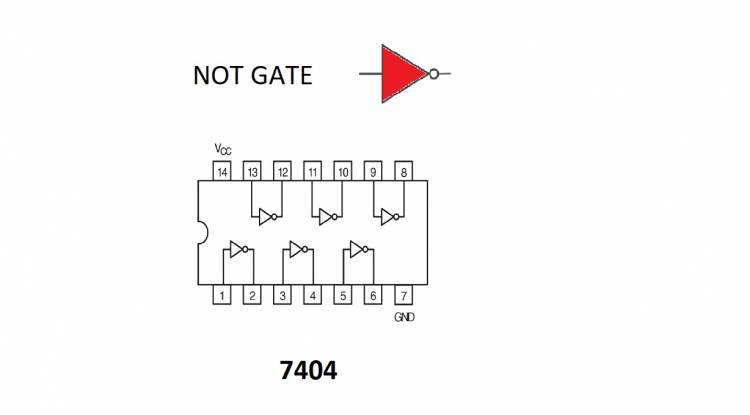
NOT is the basic logic element that produces the inverse of the input signal as output. That is, the output is "0" if the input signal is "1", and the output is "1" if the input signal is "0". Simply, it gives the inverse of the input signal.
2. Buffer:
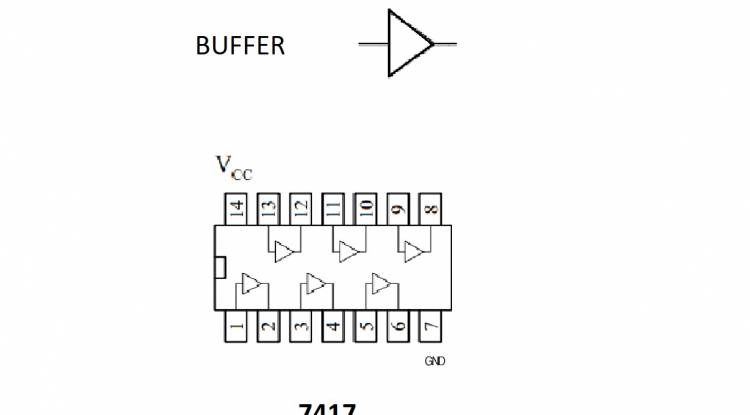
Buffer is the element that transmits the input signal directly to the output. That is, what the input signal is, the output will be the same. The buffer is used when the input signal needs to be amplified or amplified. It is especially useful when the input signal needs to be transmitted without damaging other circuits.
3. Schmitt Trigger:
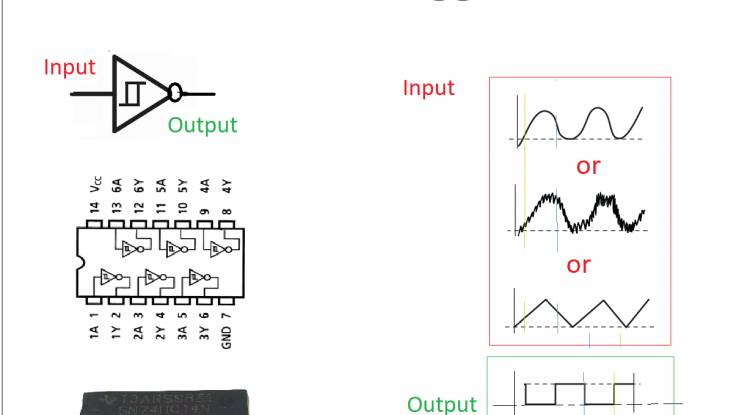
Schmitt trigger is an element that determines the output of the input signal using the upper and lower threshold values. This is useful for avoiding ripples when the input signal is rising or falling slowly. The most distinctive feature of the Schmitt trigger is that it includes a feature called hysteresis. This means that the output has different thresholds for low-to-high transition and high-to-low transition. In this way, the output state does not change until the input signal exceeds a certain threshold, thus reducing the effect of noise and fluctuations.
In summary:
NOT outputs the inverse of the input.
The buffer transmits the input signal to the output in an amplified form.
The Schmitt trigger reduces the fluctuations of the input signal with its hysteresis feature and controls its output with certain threshold values.