USB (Universal Serial Bus) Standards
USB (Universal Serial Bus) standards specify a universal connection standard used for interconnectivity and data transmission. USB standards have evolved over time, starting with USB 1.0, and have been released in different versions. Here are the main versions of the USB standards:
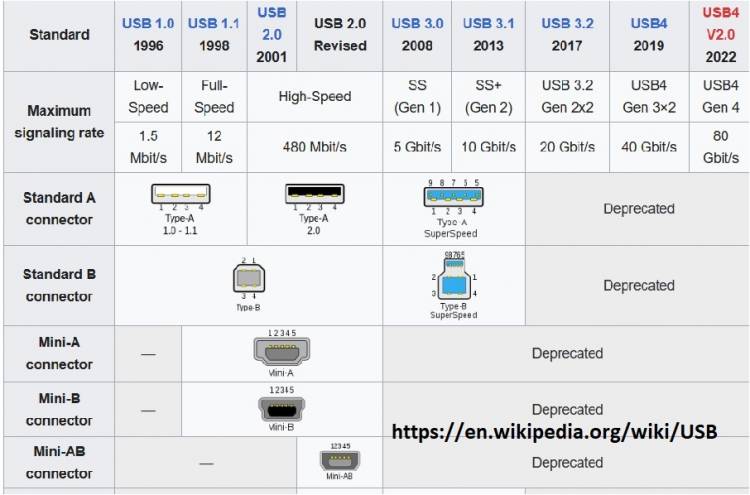
USB 1.0: One of the first USB standards. Versions 1.0 and 1.1 are available. The maximum data transfer rate is 12 Mbps.
USB 2.0: The successor to USB 1.0, this standard provides a higher data transfer rate. The maximum data transfer rate is 480 Mbps.
USB 3.0: An enhanced version of USB 2.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB. The maximum data transfer rate is 5 Gbps. USB 3.0 ports are also backward compatible with USB 2.0 devices.
USB 3.1: A faster version of USB 3.0. It has two sub-versions: USB 3.1 Gen 1 (5 Gbps data transfer rate) and USB 3.1 Gen 2 (10 Gbps data transfer rate).
USB 3.2: It is the next evolution of USB 3.1 and offers higher data transfer rates. There are three sub-versions: USB 3.2 Gen 1x1 (5 Gbps), USB 3.2 Gen 2x1 (10 Gbps) and USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 (20 Gbps).
USB 4.0: It is the latest USB standard and offers data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps. It also supports Thunderbolt 3 technology and provides backward compatibility.
USB standards have evolved over time in terms of speed and features and are divided into different speed classes. Newer USB devices are generally backward compatible and support the previous version, but the maximum speed is determined by the highest USB version they are connected to.
USB Pins
Depending on the versions of the USB standards, the number of pins has also changed. Here are the basic pin counts in USB standards:
USB 1.0/1.1: USB 1.0 and 1.1 versions use four physical pins. These are called VCC (+5V power), D- (data line negative), D+ (data line positive), and GND (ground).
USB 2.0: USB 2.0 uses the same four-pin structure: VCC, D-, D+ and GND.
USB 3.0: USB 3.0 includes additional pins besides USB 2.0. It uses 9 pins in total: VCC, D-, D+, GND as well as SS TX+ (SuperSpeed data line positive) and SS TX- (SuperSpeed data line negative) with SS (SuperSpeed) pair and SS RX+ (SuperSpeed data line positive) and SS RX- (SuperSpeed uplink negative).
USB Type-C: The USB Type-C connector is a type of connector used in USB 3.1 and later standards. This connector offers versatility and a smaller form factor. The number of pins is more in the USB Type-C connector and the pin structures have different functions.
With the development of USB standards, pin numbers and structures have changed. USB Type-C is a modern standard that offers a more flexible and versatile connection and includes more pins.
USB Connector Types
There are several types of USB connectors used in accordance with USB standards. Here are the commonly used types of USB connectors:
USB Type-A: This is the most common type of USB connector and is found on computers, laptops, USB hubs, and various USB devices. Typically used in accordance with USB 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 standards.
USB Type-B: This connector type is often used in devices such as printers, scanners, and some external hard drives. USB Type-B connectors are available in different sizes in accordance with USB 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0 standards. For example, USB 2.0 and 3.0 have variants of Type-B Standard, Mini-B, and Micro-B.
USB Type-C: USB Type-C is a type of connector used in modern USB standards. This connector has a reversible design, meaning it can be inserted in either direction. The USB Type-C connector is used for high-speed data transfer and power delivery, such as USB 3.1, 3.2, and USB 4.0. It can also carry other protocols such as HDMI, DisplayPort and Thunderbolt by supporting alternate modes.
These three main types of USB connectors are the most common. Apart from these, Micro-USB connectors for USB On-The-Go (USB OTG) and some special purpose connectors are also available. However, USB Type-A, Type-B, and Type-C are generally the most common and used connector types.