Bioelectronics: Biology and Electronics
Health Technologies and Sensors of the Future
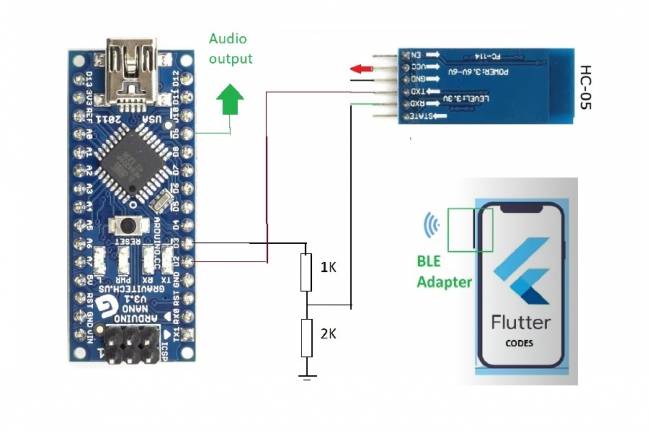
Bioelectronics is a multidisciplinary field that refers to the combination of biological systems and electronic technologies. The main goal in this field is to understand the functioning of biological organisms and interact with biological systems through advanced electronic devices.
Bioelectronics has many different application areas and is used in many fields such as the healthcare industry, medicine, biotechnology and environmental sciences. Here are some basic topics related to bioelectronics:
1. Biosensors: Biosensors are devices used to collect information from biological samples and convert this information into electrical signals. For example, they can be used to measure blood sugar levels or determine DNA sequences.
2. Bioimplants: Bioelectronics also relates to implants placed inside the human body. These implants are used for many different purposes, from medical applications such as pacemakers to brain implants.
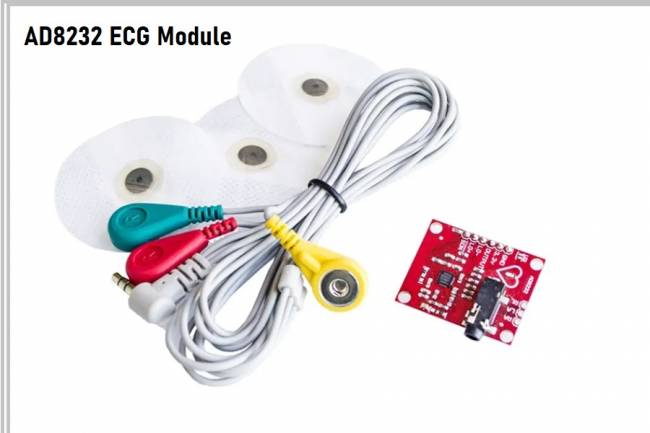
3. Monitoring Bioelectrical Signals: Monitoring bioelectrical signals using methods such as electrocardiography (ECG) and electroencephalography (EEG) is an important application area in bioelectronics. These signals are used in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
4. Bionanotechnology: Nanotechnology also plays a big role in bioelectronics. Nanomaterials and nanotechnology can enhance the development of biosensors and the capacity to interact with biological systems.
5. Bioactive Materials: Bioactive materials are electronic materials that interact with biological systems and are used in applications such as tissue engineering or drug delivery.
6. Biointeraction and Biointerfaces: Bioelectronics is a field that studies the interaction between electronic devices and biological organisms. This is important to ensure safe and effective communication between biological systems and electronic devices.
Bioelectronics is a field with great potential in health diagnosis and treatment, biotechnology, medical research, environmental monitoring, and many other fields. Developments in this field can make significant contributions to improving human health and quality of life.
Bioelectronic sensors can be used for many different applications and are available in many different makes and models. Some examples of bioelectronic sensors:
1. Glucose Sensors:
Dexcom G6: This sensor is a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device and is used in diabetes management. It allows users to continuously monitor their blood glucose levels.
2. ECG Sensors:
AliveCor KardiaMobile: It is a portable ECG device and helps users monitor their own heartbeat. The device is integrated with a portable smartphone application.
3. Hematocrit Sensors:
i-STAT Hematocrit Test Cartridges: These sensors are used with the i-STAT portable blood analyzer and quickly measure hematocrit levels.
4. Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) Sensors:
Masimo Rad-97: This sensor is used with patient monitors and portable oxygen saturation meters. Masimo offers many different SpO2 sensors.
5. Electroencephalography (EEG) Sensors:
NeuroSky MindWave Mobile: This portable EEG sensor is aimed at people who want to monitor brain activity and use it for applications such as meditation or attention training.
6. Biosensor Arrays:
Quanterix Simoa: This biosensor technology has ultralow analytical sensitivity and is used for the diagnosis of neurological disorders, cancers and other health conditions.
7. DNA Sequencing Sensors:
Illumina MiSeq: This DNA sequencing device is used to produce high-quality genetic data and plays an important role in genetic research and medical diagnoses.