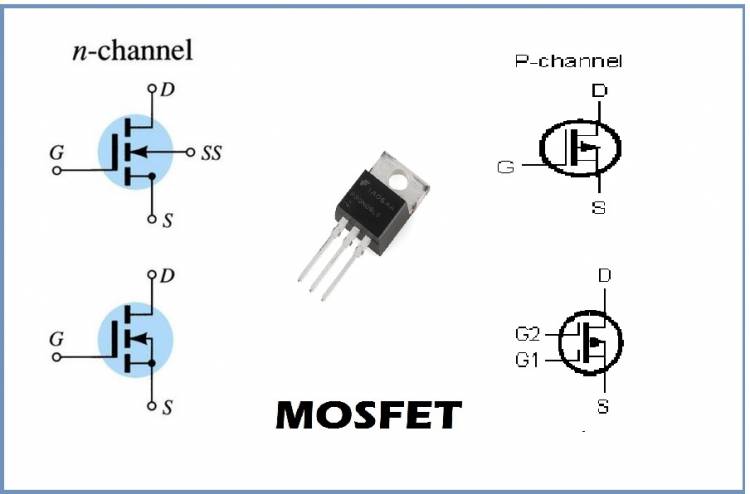
What is MOSFET?
MOSFET is short for Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor. MOSFET is a type of transistor that provides switching and amplification functions in electronic circuits using the properties of semiconductors.
A MOSFET is a device with three terminals: source, drain, and gate. The voltage applied to the door controls the conductivity of the device. The higher the voltage applied to the gate, the higher the conductivity of the device.
MOSFETs consume less power and are less noisy compared to bipolar transistors (BJTs). Also, MOSFETs have high input impedance and low output impedance, so they offer better signal processing performance than other types of transistors.
What is the difference between MOSFET and FET?
The terms MOSFET and FET (Field Effect Transistor) refer to the types of transistors that are related to each other. MOSFET is a subset of FET.
FETs are a type of transistor made with electrodes placed on a thin layer of insulator on semiconductor materials. By applying an electric field on this insulating layer, the flow of electrons on the semiconductor can be controlled.
MOSFETs are also a type of FET, but they use a metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) as the insulating layer. The working principle of MOSFETs is the same as FETs, but MOSFETs have higher input impedance and lower input current as the capacitance to the insulator layer is high. Therefore, MOSFETs operate more sensitively, more efficiently, and faster than other FETs.
How many types of MOSFETs are there?
MOSFETs are produced in different types due to different semiconductor materials, structural designs and functions. Functionally, MOSFETs fall into two main categories: enhancement MOSFETs and depletion MOSFETs.
Enhancement MOSFETs require amplification to create a channel that allows current flow when a high impedance input signal is applied. Depletion MOSFETs, on the other hand, stop current flow by destroying the channel when a negative voltage is applied.
Structurally, MOSFETs come in a variety of designs, but the most common are metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFET) and double-gate MOSFETs (DMOS). Other types include surface area effect transistors (UMOS), MOSFETs designed for human-like robotic touch sensors (HT-MOS), and MOSFETs capable of operating at high temperatures (HT-MOSFET).
What types of circuits are MOSFETs used in?
Power supplies: MOSFETs are used in power supplies used in high current and voltage applications. In these applications, MOSFETs provide high efficiency and low power loss.
Amplifiers: MOSFETs are used in audio and radio frequency (RF) amplifiers. In these applications, MOSFETs provide high gain and low noise characteristics.
Switching circuits: MOSFETs are used in circuits that require an on/off function. For example, MOSFETs can be used in a light strip circuit used to control LEDs.
Solar power systems: MOSFETs are used in power inverters used in solar power systems. In these applications, MOSFETs provide efficiency in power conversion.
Microprocessors: MOSFETs are used in memory cells and other logic circuits used in microprocessors.
Automotive electronics: MOSFETs are used in a variety of electronic applications used in the automobile industry. For example, applications such as interior lighting, air conditioning and engine control use MOSFETs.