What is Frequency Modulation?
What are the fundamentals of frequency modulation?
Frequency Modulation (FM) is a type of modulation used as a communication system or broadcasting method. FM refers to changing the frequency on a carrier wave according to the characteristics of a modulating signal (usually voice, data or video).
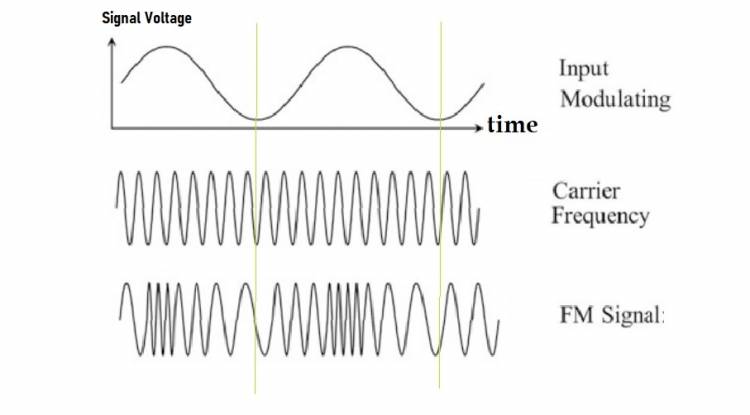
In FM, the amplitude or amplitude of the modulating signal is not changed; instead, the frequency of the signal is changed. As the frequency of the modulating signal increases or decreases, the carrier wave frequency shifts up or down accordingly. This frequency change enables communication by transmitting the properties of the modulating signal on the carrier wave.
The following illustration describes how the central frequency changes according to the voltage level of a signal applied to the FM transmitter input:
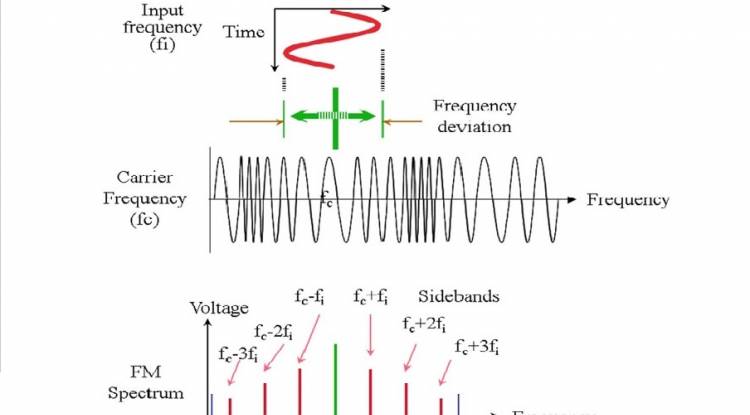
FM is mainly used in radio broadcasting and voice transmission. For example, an FM radio station modulates the audio signal, creating a frequency shift on the carrier wave. This frequency shift ensures that the original sound is obtained on the receiver side. The advantages of FM modulation include good sound quality, low interference and interference sensitivity, and stability over long transmission distances.
FM modulation is an important technology used in electronic communication and communication systems and is widely used in many different application areas.
Below is the diagram of an FM transmitter that we have made on our site before.
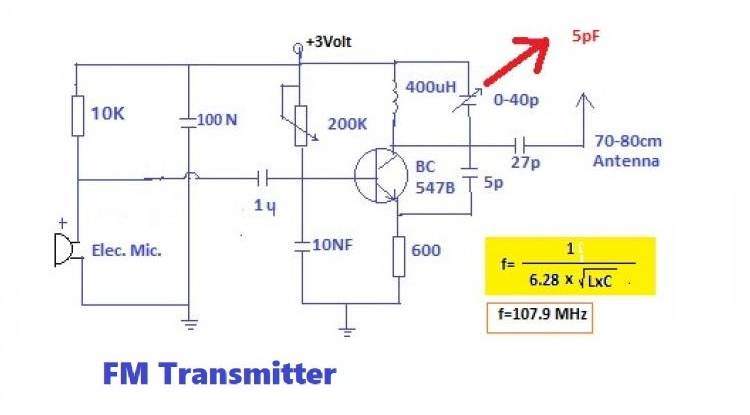
In the circuit, the signal changes occurring in the electret microphone shift the center frequency on the LC connected to the collector of the BC547 transistor. The central frequency is 107.9 MHz.
Click here to access the single transistor FM transmitter circuit article: